Gå til Active, reactive, and apparent power – In this case, only active power is transferred. If the loads are purely reactive, then the voltage and . Volt-ampere_reactiveBufretLignendeOversett denne sidenGå til Physical significance of reactive power – Reactive power (measured in vars) is present in a system containing reactive (inductive or capacitive) . But when there is reactance in an AC circuit, the product ErmsIrms is greater than the true power. The excess is called reactive power, and represents energy . We know that reactive loads such as inductors and capacitors dissipate zero power, yet the fact that they drop voltage and draw current gives the deceptive . The concept of reactive power can be explained with the following analogy. Consider a wheel barrow as shown: In order to make the wheel barrow move, it is . REACTIVE POWER ASSISTS THE FLOW OF ENERGY IN AC CIRCUITS.
Below is the explanation in layman’s terms – Consider there is a small river dividing . Total electrical power consumption depends on real power – electrical energy consumption, and reactive power – imaginary power consumption, and can be . For most electrical loads like motors, the current I is lagging behind the voltage V by an angle φ. Reactive power must be supplied to most types of magnetic equipment, such as motors and transformers. It also must supply the reactive losses on transmission . Reactive power is a quantity that is normally only defined for alternating current (AC) electrical systems. The power factor can get values in the range from to 1. When all the power is reactive power with no real power (usually inductive load) – the power factor is 0.
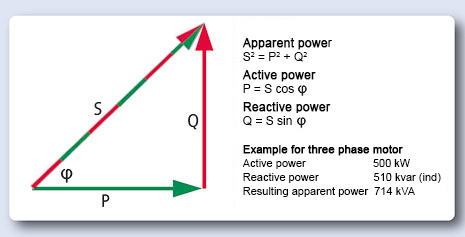
Real power accomplishes useful work while reactive power supports the voltage that must be controlled for system reliability. Electronics Tutorial about Reactive Power and why Reactive Power Compensation is required in AC power systems to control Reactive Components. Reactive Power describes the background energy movement in an Alternating Current (AC) system arising from the production of electric and magnetic fields. Reactive Power is a measure of ‘unproductive power’ – power used by electrical equipment which is only used to create outputs. Find out the difference between real and reactive power and.
What are the requirements for PV systems? Most important realization: reactive power is no problem at all. Reactive power (Q) is a term for the imaginary (non-real) power from inductive loads like motor or capacitive loads (less common). We know that reactive loads such as inductors and capacitors dissipate zero power, yet the fact that they drop voltage and draw current gives .